Due to rhythmical discharge of impulses that can originate in any part of the heart and spread throughout the heart, the heart rate can become rapid in paroxysms – paroxysmal tachycardia – which can last for a few seconds, few minutes, few hours or much longer.
There are two types of paroxysmal tachycardia:-
- Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
- Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
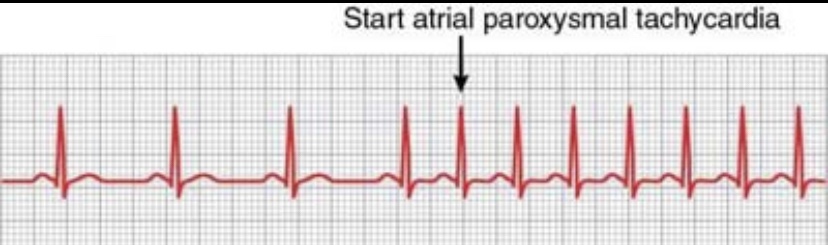
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia: The responsible rapid abnormal impulses are in the atria. On ECG, the P wave may be inverted or superimposed on the normal T wave.
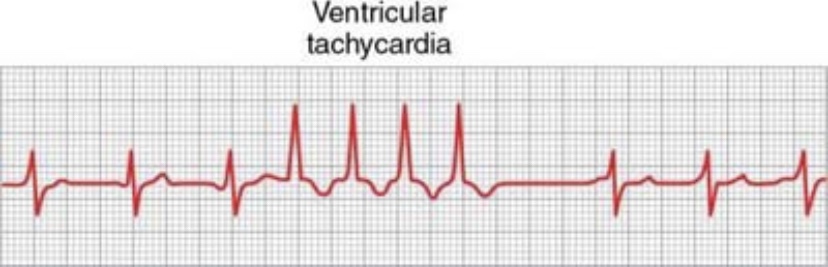
Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia: The responsible rapid abnormal impulses are in the ventricles. Ok ECG, a series of ventricular premature beats are seen occurring one after another without any normal beats interspersed. Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia is a serious condition, as it usually happens in the presence of considerable ischemic damage and lead to the potentially fatal condition of ventricular fibrillation.
Treatment:
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs like amiodarone and lidocaine
- Cardioversion
- Vagal reflex
Amiodarone prolongs the action potential and refractory period in cardiac muscle and slows A-V conduction.
Lidocaine reduces sodium permeability of the cardiac muscle membrane during generation of the action potential.
Vagal reflex can be elicited by pressing on the neck in the regions of the carotid sinus and can depress the heart rate.
Leave a comment